|
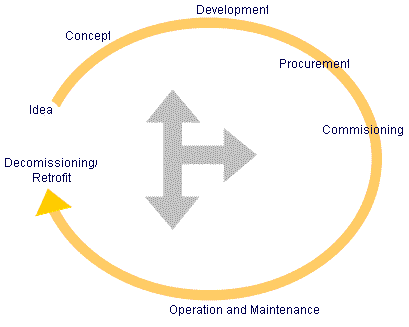
Appraising alternative system
solutions in the evaluation and concept phase |
 |
Risk analyses:
hazard analysis, risk definition, risk assessment, confirmation of
acceptance criteria |
 |
System analyses and optimization of
the system structure (redundancy, safeguards, diagnostics, maintainability),
operating sequence (in case of disturbances and emergences), ergonomic
assessment/ operation, spare part organization, logistics |
 |
Specification of requirements to
system safety, reliability and availability |
 |
Verification of the required safety,
reliability and availability
by probabilistic analyses and/or deterministic methods (conformance with
safety standards) |
 |
Verification of the required safety,
reliability and availability
by statistical methods
using service and/or life tests data |
 |
Development of economical maintenance
methods and construction of the maintenance plan |
 |
Building a cost model for investment
cost, operation and support costs
in order to estimate alternative system, operating and maintenance solutions (Life Cycle Costing) |
 |
Building a safety plan for
emergences, event feed backs and measurement planning |
 |
Building an action plan for
disruptions: analysis
of disturbance scenarios, establishing operating sequences and recovery
procedures. Building check lists and instructions. |
Brief (non-mathematical) Explanation of Terms
Life time, failure safety,
availability... Always clear what it
means?
The term around reliability and safety are often used misunderstandingly.
Here is a short explanation, which do not claim to be precisely. But, hopefully,
is commonly understandable. Anyway, descriptions are conform with common
standards.
RAMS: Reliability, Availability, Maintainability, Safety
RAMS Terms,
Typical questionings and
commonly used measurements |
|
Move the mouse pointer over the terms |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Risk
Risk
in addition to safety, considers the severity of safety critical failures and weights them according to their acceptance
Are consequences for humans and the environment tolerable, accesptable, undisirable, unaccesptable, ... ?
Frequency of occurence x hazard severity
Useful Life
Useful Life
is the intended service life of a system or a component, during which the specified reliability,
safety and availability are met under the stated maintenance activities
How long is the system/ the component (economically)
maintainable, are spares obtainable, etc. ?
Service life in years,
Number of operating cycles,
etc.
|
|
 |
Safety (S)
Safety (S)
is defined as reliability, but considers safety critical failures
How many dangerous/ critical/... failures ?
As for reliability:
Safety critical failure rate
MTBSF
MTTSF
Availability (A)
Availability (A)
in addition to reliability, considers the
down time and preventive maintenance
Will it really work when I need it ?
Ratio of available operating time to observed mission time (a probability)
(Unavailability is the complement:
1 - A)
|
Reliability (R)
Reliability (R)
is associated with freedom from failures (no malfunctions or component breakdowns)
How many disturbances, interruptions, repairs, ... ?
Number of failures per time unit, e.g. per year (failure rate)
mean time between failures (MTBF)
mean time to failure (MTTF)
Maintainability (M)
Maintainability (M)
has an important influence on availability and the
maintenance cost
Items easily replaceable, repairable, testable, etc. ?
Mean time to repair (MTTR),
Mainteannce intervals,
Mean time to maintain (MTTM), etc.
Maintenance
Maintenance
comprises all actions intended to retain and restore normalcy
|
 |
|
|
 |
| |